
The Underappreciated Role of Magnesium in Our Health
Magnesium is often overshadowed by more well-known minerals like calcium and potassium, but it plays an equally vital role in our health. This mineral is involved in over 600 biochemical reactions in the body, aiding everything from energy production to muscle function. For individuals grappling with type 2 diabetes, magnesium’s importance cannot be overstated. Research suggests that adequate magnesium levels can help improve insulin sensitivity and glucose control, making it a crucial ally for those managing this condition.
Why Magnesium Matters for Blood Sugar Management
Magnesium impacts how our bodies metabolize glucose, directly influencing insulin action. Studies have shown that low magnesium levels are often linked with insulin resistance — a key factor in the development of type 2 diabetes. By supporting pancreatic function and modulating insulin signaling pathways, magnesium may reduce the risk of developing diabetes and aid in the management of those already diagnosed. People with adequate magnesium intake may lower their risk of developing type 2 diabetes by as much as 30% compared to those with lower levels.
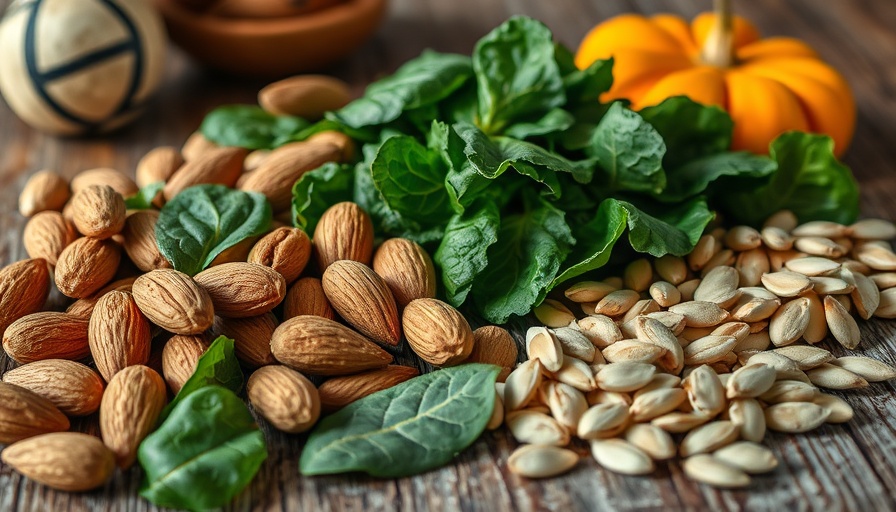
Sources of Magnesium: Best Foods to Incorporate
To boost magnesium intake, consider incorporating these nutrient-rich foods into your diet:
- Green Leafy Vegetables: Foods like spinach and kale are rich in magnesium and versatile for salads or smoothies.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds and pumpkin seeds make great snacks and can easily be added to meals for an extra nutrient punch.
- Whole Grains: Quinoa, brown rice, and oats are excellent magnesium sources and provide additional fiber benefits.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are not only rich in magnesium but also protein, making them an excellent choice for vegetarians.
- Other Sources: Don’t overlook dark chocolate and avocados — they’re not only delicious but also contribute to your magnesium intake.
Understanding Magnesium Deficiency
Unfortunately, magnesium deficiency is alarmingly common, impacting around half of the adult population to varying degrees. Symptoms of low magnesium can include muscle cramps, fatigue, and irritability. Such deficiency may interfere with effective blood sugar management, making it essential to ensure your magnesium levels are sufficient. Individuals who consume a diet high in processed foods, or those who experience gastrointestinal issues, are at a greater risk of developing magnesium deficiency.
Supplementing Magnesium: When and How?
While dietary sources are ideal for most people, supplementing with magnesium can be beneficial, especially for those who struggle to meet their daily requirements. Various forms of magnesium supplements are available, including magnesium citrate, oxide, and glycinate. However, it's vital to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen, as too much magnesium can lead to adverse effects, such as digestive discomfort.
Practical Tips for Increasing Magnesium Intake
To incorporate more magnesium into your life, try these practical tips:
- Start your day with a breakfast that includes whole grains and fruits rich in magnesium, such as oatmeal topped with banana.
- Keep healthy snacks handy — a small handful of almonds can provide a great boost of magnesium.
- Experiment with new recipes that highlight magnesium-rich foods; a spinach salad or quinoa bowl can be both flavorful and nutritious.
- Consider cooking with mineral-rich broths or making smoothies to blend in greens and seeds effortlessly.
Take Action for Your Health Today
The relationship between magnesium and diabetes management shows the remarkable power of nutrition in disease prevention and wellness. By taking proactive steps to optimize your magnesium intake, you can significantly improve your well-being. Don’t hesitate to consult health professionals for personalized advice tailored to your health needs.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment